ملف:Karmarkar.svg
من testwiki
اذهب إلى التنقل
اذهب إلى البحث

حجم معاينة PNG لذلك الملف ذي الامتداد SVG: ٧٢٠ × ٥٤٠ بكسل. الأبعاد الأخرى: ٣٢٠ × ٢٤٠ بكسل | ٦٤٠ × ٤٨٠ بكسل | ١٬٠٢٤ × ٧٦٨ بكسل | ١٬٢٨٠ × ٩٦٠ بكسل | ٢٬٥٦٠ × ١٬٩٢٠ بكسل.
الملف الأصلي (ملف SVG، أبعاده ٧٢٠ × ٥٤٠ بكسل، حجم الملف: ٤٣ كيلوبايت)
هذا الملف من ويكيميديا كومنز ويمكن استخدامه بواسطة المشاريع الأخرى. الوصف على صفحة وصف الملف هناك معروض بالأسفل.
ملخص
| الوصفKarmarkar.svg |
English: Solution of example LP in Karmarkar's algorithm.
Blue lines show the constraints, Red shows each iteration of the algorithm. |
| التاريخ | |
| المصدر | عمل شخصي |
| المؤلف | Gjacquenot |
| SVG منشأ الملف InfoField |
ترخيص
Gjacquenot، صاحب حقوق التأليف والنشر لهذا العمل، أنشر هذا العمل تحت الرخصة التالية:
هذا الملفُّ مُرخَّصٌ برخصة المشاع الإبداعي الدَّوليَّة المُلزِمة بنسب العمل إلى مُؤَلِّفه وبترخيص المُشتقَّات بالمثل 4.0.
نسب العمل لمُؤَلِّفه:
Gjacquenot
- يحقُّ لك:
- مشاركة العمل – نسخ العمل وتوزيعه وبثُّه
- إعادة إنتاج العمل – تعديل العمل
- حسب الشروط التالية:
- نسب العمل إلى مُؤَلِّفه – يلزم نسب العمل إلى مُؤَلِّفه بشكل مناسب وتوفير رابط للرخصة وتحديد ما إذا أجريت تغييرات. بالإمكان القيام بذلك بأية طريقة معقولة، ولكن ليس بأية طريقة تشير إلى أن المرخِّص يوافقك على الاستعمال.
- الإلزام بترخيص المُشتقات بالمثل – إذا أعدت إنتاج المواد أو غيرت فيها، فيلزم أن تنشر مساهماتك المُشتقَّة عن الأصل تحت ترخيص الأصل نفسه أو تحت ترخيص مُتوافِقٍ معه.
Source code (Python)
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#
# Python script to illustrate the convergence of Karmarkar's algorithm on
# a linear programming problem.
#
# http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Karmarkar%27s_algorithm
#
# Karmarkar's algorithm is an algorithm introduced by Narendra Karmarkar in 1984
# for solving linear programming problems. It was the first reasonably efficient
# algorithm that solves these problems in polynomial time.
#
# Karmarkar's algorithm falls within the class of interior point methods: the
# current guess for the solution does not follow the boundary of the feasible
# set as in the simplex method, but it moves through the interior of the feasible
# region, improving the approximation of the optimal solution by a definite
# fraction with every iteration, and converging to an optimal solution with
# rational data.
#
# Guillaume Jacquenot
# 2015-05-03
# CC-BY-SA
import numpy as np
import matplotlib
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure, show, rc, grid
class ProblemInstance():
def __init__(self):
n = 2
m = 11
self.A = np.zeros((m,n))
self.B = np.zeros((m,1))
self.C = np.array([[1],[1]])
self.A[:,1] = 1
for i in range(11):
p = 0.1*i
self.A[i,0] = 2.0*p
self.B[i,0] = p*p + 1.0
class KarmarkarAlgorithm():
def __init__(self,A,B,C):
self.maxIterations = 100
self.A = np.copy(A)
self.B = np.copy(B)
self.C = np.copy(C)
self.n = len(C)
self.m = len(B)
self.AT = A.transpose()
self.XT = None
def isConvergeCriteronSatisfied(self, epsilon = 1e-8):
if np.size(self.XT,1)<2:
return False
if np.linalg.norm(self.XT[:,-1]-self.XT[:,-2],2) < epsilon:
return True
def solve(self, X0=None):
# No check is made for unbounded problem
if X0 is None:
X0 = np.zeros((self.n,1))
k = 0
X = np.copy(X0)
self.XT = np.copy(X0)
gamma = 0.5
for _ in range(self.maxIterations):
if self.isConvergeCriteronSatisfied():
break
V = self.B-np.dot(self.A,X)
VM2 = np.linalg.matrix_power(np.diagflat(V),-2)
hx = np.dot(np.linalg.matrix_power(np.dot(np.dot(self.AT,VM2),self.A),-1),self.C)
hv = -np.dot(self.A,hx)
coeff = np.infty
for p in range(self.m):
if hv[p,0]<0:
coeff = np.min((coeff,-V[p,0]/hv[p,0]))
alpha = gamma * coeff
X += alpha*hx
self.XT = np.concatenate((self.XT,X),axis=1)
def makePlot(self,outputFilename = r'Karmarkar.svg', xs=-0.05, xe=+1.05):
rc('grid', linewidth = 1, linestyle = '-', color = '#A0A0A0')
rc('xtick', labelsize = 15)
rc('ytick', labelsize = 15)
rc('font',**{'family':'serif','serif':['Palatino'],'size':15})
rc('text', usetex=True)
fig = figure()
ax = fig.add_axes([0.12, 0.12, 0.76, 0.76])
grid(True)
ylimMin = -0.05
ylimMax = +1.05
xsOri = xs
xeOri = xe
for i in range(np.size(self.A,0)):
xs = xsOri
xe = xeOri
a = -self.A[i,0]/self.A[i,1]
b = +self.B[i,0]/self.A[i,1]
ys = a*xs+b
ye = a*xe+b
if ys>ylimMax:
ys = ylimMax
xs = (ylimMax-b)/a
if ye<ylimMin:
ye = ylimMin
xe = (ylimMin-b)/a
ax.plot([xs,xe], [ys,ye], \
lw = 1, ls = '--', color = 'b')
ax.set_xlim((xs,xe))
ax.plot(self.XT[0,:], self.XT[1,:], \
lw = 1, ls = '-', color = 'r', marker = '.')
ax.plot(self.XT[0,-1], self.XT[1,-1], \
lw = 1, ls = '-', color = 'r', marker = 'o')
ax.set_xlim((ylimMin,ylimMax))
ax.set_ylim((ylimMin,ylimMax))
ax.set_aspect('equal')
ax.set_xlabel('$x_1$',rotation = 0)
ax.set_ylabel('$x_2$',rotation = 0)
ax.set_title(r'$\max x_1+x_2\textrm{ s.t. }2px_1+x_2\le p^2+1\textrm{, }\forall p \in [0.0,0.1,...,1.0]$',
fontsize=15)
fig.savefig(outputFilename)
fig.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
p = ProblemInstance()
k = KarmarkarAlgorithm(p.A,p.B,p.C)
k.solve(X0 = np.zeros((2,1)))
k.makePlot(outputFilename = r'Karmarkar.svg', xs=-0.05, xe=+1.05)
الشروحات
أضف شرحاً من سطر واحد لما يُمثِّله هذا الملف
العناصر المصورة في هذا الملف
يُصوِّر
قيمة ما بدون عنصر ويكي بيانات
٣ مايو 2015
تاريخ الملف
اضغط على زمن/تاريخ لرؤية الملف كما بدا في هذا الزمن.
| زمن/تاريخ | صورة مصغرة | الأبعاد | مستخدم | تعليق | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| حالي | ١٦:٣٤، ٢٢ نوفمبر ٢٠١٧ | 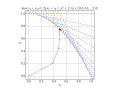 | ٧٢٠ × ٥٤٠ (٤٣ كيلوبايت) | wikimediacommons>DutchCanadian | The right hand side for the constraints appears to be p<sup>2</sup>+1, rather than p<sup>2</sup>, going by both the plot and the code (note the line <tt>self.B[i,0] = p*p + 1.0</tt>). Updated the header line. |
استخدام الملف
الصفحة التالية تستخدم هذا الملف: